
Hedge accounting, which is optional, appeals to companies involved in hedging activities. Not all economic hedging relationships are hedge accounting eligible and the qualifying criteria are complex and subject to strict documentation. With the introduction of IFRS 91 in 2018, the eligibility of hedge accounting has significantly expanded and here we summarize how hedge accounting works and key differences between IFRS 9 and ASC 815. Disclosures related to foreign currency hedge accounting are integral to providing transparency and insight into a company’s risk management strategies. These disclosures help stakeholders understand the nature and extent of the risks being hedged, the instruments used, and the effectiveness of these hedging activities. By offering a detailed view of hedging relationships, companies can enhance the credibility of their financial statements and foster investor confidence.

Treasury & Risk
For instance, Company A might enter into a forward contract to sell euros and buy US dollars at a predetermined rate, thus mitigating the impact of EUR depreciation on its investment. A fair value hedge is an instrument used to mitigate the company’s exposure to volatility and fluctuations in the fair value of the asset or liability. To be eligible for hedge accounting, changes in the fair value of the underlying asset or liability must have the potential to affect the company’s earnings. A firm commitment to acquire a business in a business combination cannot be a hedged item, except for foreign currency risk. Risks other than foreign currency risk cannot be specifically identified and measured and are considered to be general business risks (IFRS 9.B6.3.1). So in short, simplified hedge accounting provides more leeway on the timing of formal hedge documentation while still requiring companies to eventually provide it.
Guide to Hedge Accounting under Ind AS 109/IFRS 9
- Hedge effectiveness is key to ensuring that a hedging instrument adequately offsets the hedged risk.
- The Critical Terms Match is a key concept in assessing hedge effectiveness within frameworks like International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) and Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
- Any format may be acceptable as long as the documentation includes the contents identified above.
- By synchronizing the timing of gain/loss recognition in this manner, the natural offset between the hedging instrument and hedged item helps smooth out earnings fluctuations.
- The adjustment to the carrying value of a hedged item is often referred to as a ‘basis adjustment’.
Understanding hedge accounting is important for businesses that engage in complex financial transactions. It allows them to mitigate potential volatility in earnings due to market fluctuations. A very common occurrence of hedge accounting is Certified Public Accountant when companies seek to hedge their foreign exchange risk.
- In designing the modules, they have focused on the relevance and impact of IFRS, in theory and in practice, for banks specifically.
- Yet, hedge accounting under IAS 39 can help decrease the hedging tool’s volatility.
- It may occur that the transactions of a business to be acquired qualify as a hedged item, provided they can be considered a highly probable forecast transaction from the perspective of the acquirer.
- We shall try to deal with this topic in further detail in our subsequent write-ups.
- It attempts to remove volatility created by adjusting a financial instrument’s value.
- As per the International Financial Reporting Standards, such instruments need to be reported at fair values in the financial statements, at each reporting date, using ‘mark-to-market’ value.
- But they need to be prepared to invest appropriate resources and develop sufficient capabilities to meet hedge accounting requirements on an ongoing basis.
Order to Cash
This means changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedging instrument are expected to offset changes in the fair value or cash flows of the hedged item. A precise match between the terms of the hedging instrument and the hedged item simplifies hedge accounting. When terms align, the hedge is often deemed highly effective, enabling the application of hedge accounting without extensive quantitative testing. This is especially important in cash flow hedges, where the timing and amount of cash flows must match.
- You can complete this course without having completed the other IFRS 9 e-learnings in the series, but it is advisable to complete the module introducing the concepts of IFRS 9 first.
- But in hedge accounting, they would be considered a bundle and accounted for.
- In the provided example, the aggregate exposure comprising the combination of the debt instrument plus the interest rate swap would be eligible to be designated as the hedged item.
- For a “cash flow hedge”, some of the derivative volatility is placed into a separate component of the entity’s equity called the cash flow hedge reserve.
- This documentation must be completed whenever a new hedging relationship is designated.
Hedge accounting of the foreign currency risk arising from a net investment in a foreign operation will apply only when the net assets of that foreign operation are consolidated. Changing market conditions naturally lead to fluctuations in fair and cash flows, both in the hedged time and the hedge instrument used. The use of hedge accounting requires detailed disclosures within financial statements to inform stakeholders about hedging activities, goals, and results. Managing hedge accounting can be complex, but the right tools streamline operations. Accounting automation software accelerate key processes, ensuring accurate reflection of hedge accounting in financial statements.

2. Accounting for hedges
The risk being hedged here is a change in the fair value of asset or liability or an unrecognized firm commitment attributable to a particular risk. The proposed ASU is intended to improve alignment of hedge accounting guidance with risk management activities. Since then, the changes have been focused on reducing operational burden, expanding the circumstances in which hedge accounting is permissible and better reflecting risk management practices. The simplified hedge accounting approach relaxes some of the strict documentation requirements for hedge accounting under accounting standards like IFRS 9 or ASC 815. Prospective tests look forward, and determine if an instrument is going to be effective. To effectively hedge, an instrument must be expected to be highly effective for periods of time.
The new standard which defines hedge accounting in a fresher perspective would reduce the time, effort, and expense of the businesses. At the same time, investors would receive accurate and timely financial reporting. Though there would be detailed initial assessments, disclosures, risk management assessment, financial impact assessment, and data requirements, it would help is to attain the real value of the information. On 1 January, Entity A decides to purchase a piece of equipment, with the transaction expected to take place on 30 June of the same year. Entity A’s functional currency is the EUR, and the equipment will cost USD 300k. The premium paid amounts to EUR 10k and represents the time value of the option.
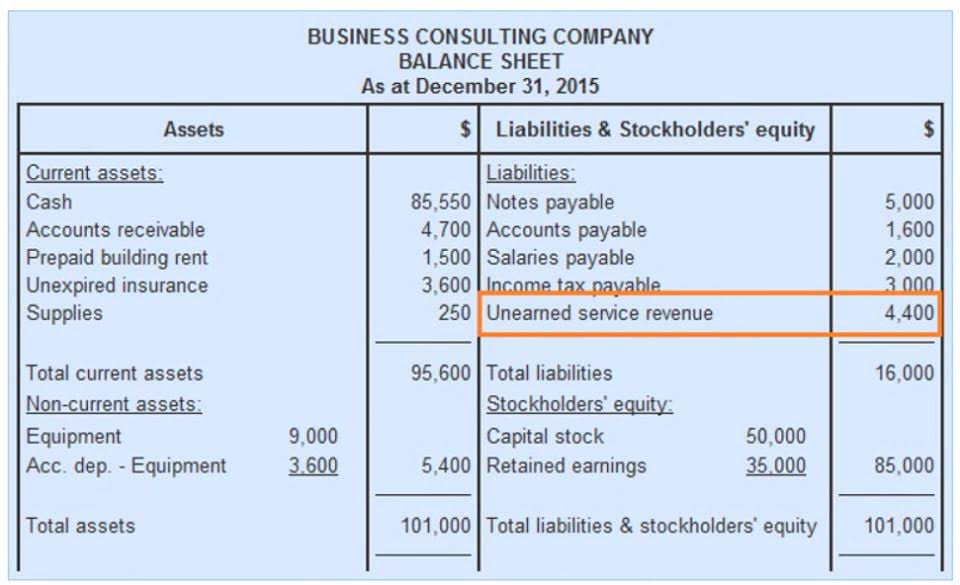
As we’ve discussed above, it’s important that businesses using hedge accounting can ensure that the hedge used accurately offsets changes in the fair value of cash flows of the hedged items. IFRS 9 is the international accounting standard that governs hedge accounting. It allows companies more flexibility than its predecessor, IAS 39, by simplifying the process for determining hedge effectiveness. Under IFRS 9, companies can use qualitative methods to assess the relationship between the hedging instrument and the hedged item, as long as the hedge is expected to be highly effective. Once you qualify the hedge, record the hedging instruments on the balance sheet.

While hedge accounting is not a mandatory practice, it’s a valuable tool for businesses when it comes to financial risk management. Due to this, a lot of businesses leverage hedge accounting to offset the value of volatile assets and liabilities. 1 For a fair value hedge, the offset is achieved either by marking-to-market an asset or a liability which offsets the P&L movement of the derivative. For a “cash flow hedge”, some of the derivative volatility is placed into a separate component of the entity’s equity called the cash flow hedge reserve. A key requirement for hedge effectiveness is an economic relationship between the hedged item and the hedging instrument. This means that their values generally move in opposite directions in response to the same risk (the hedged https://www.bookstime.com/articles/better-bookkeepers risk).

